Product managers are responsible for defining the vision, strategy, and roadmap for their products. A product roadmap is a high-level visual summary that outlines the product strategy and the direction of the product over time. It is an essential tool for any product manager, as it helps them communicate the product vision and strategy to stakeholders and the team. In this article, we will discuss what a roadmap is, how to start building it, the necessary tools, and best practices.
What is a Roadmap
A product roadmap is a high-level strategic document that communicates the product vision, strategy, and direction to stakeholders and the team. It outlines the necessary goals, objectives, and initiatives that are required to achieve the product vision.
Where to Start
Creating product roadmaps can be a daunting and challenging task because it requires a deep understanding of the product, the market, and the customer needs. They are challenging because they require constant updates and revisions as the product evolves and the market changes.
Building effective product roadmaps is a crucial step in the journey of product development. So knowing where to start and how to proceed is essential for crafting these tools to not only align your product vision but also adapt to the ever-changing market dynamics.
1. Identify your Objective
First start by clarifying the purpose of the roadmap. You need to understand if it is to align your team, inform other stakeholders, or guide product development. The objective of the roadmap will help inform what type of roadmap format you will be using and how much detail is included.
2. Understand Your Audience
You need to identify the primary audience of the roadmap and tailor it to their specific needs. This is because a roadmap designed for internal development teams can differ from roadmaps designed for high-level stakeholders.
3. Collect Data
Ensure that your roadmap is informed and thorough by creating market analysis, gathering customer feedback and assessing your resources and capabilities. This will help you develop the foundation of your roadmap.
4. Sketch a High-level Plan
Outline major goals and milestones you aim to achieve. You can think broadly about the direction of your product and the necessary steps needed to get there.
Tools You Can Use

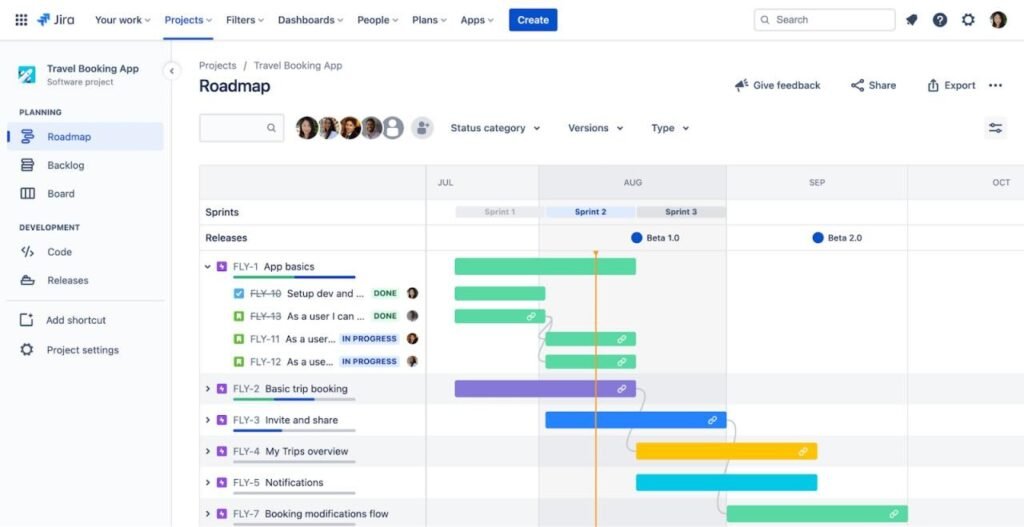
Jira
Jira offers great flexibility when it comes to workflows and allows you to set it up any way you want.
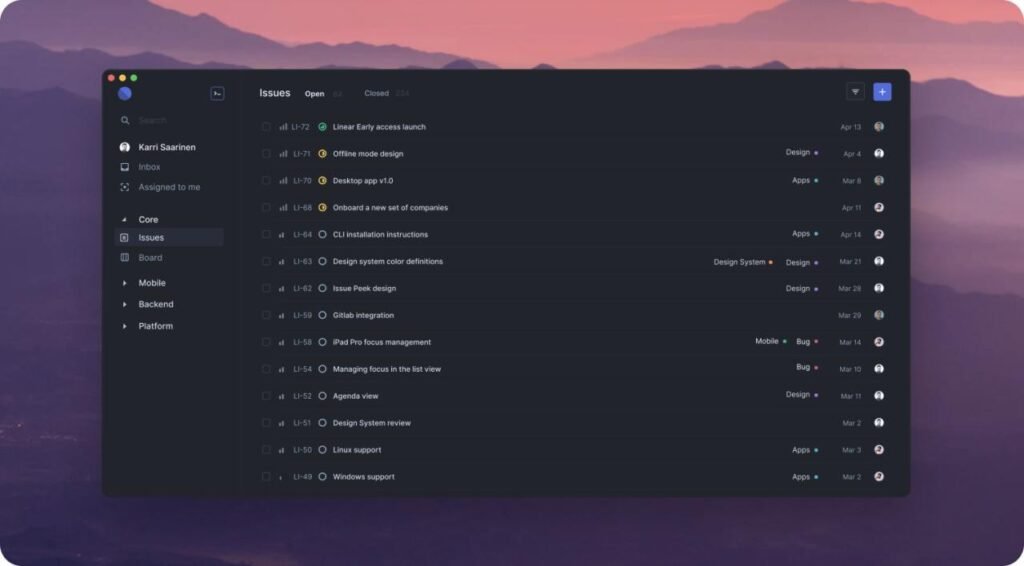
Linear
While Jira offers more flexibility with workflows, Linear offers a streamlined and intuitive UX which makes it easy for small and news teams to set up
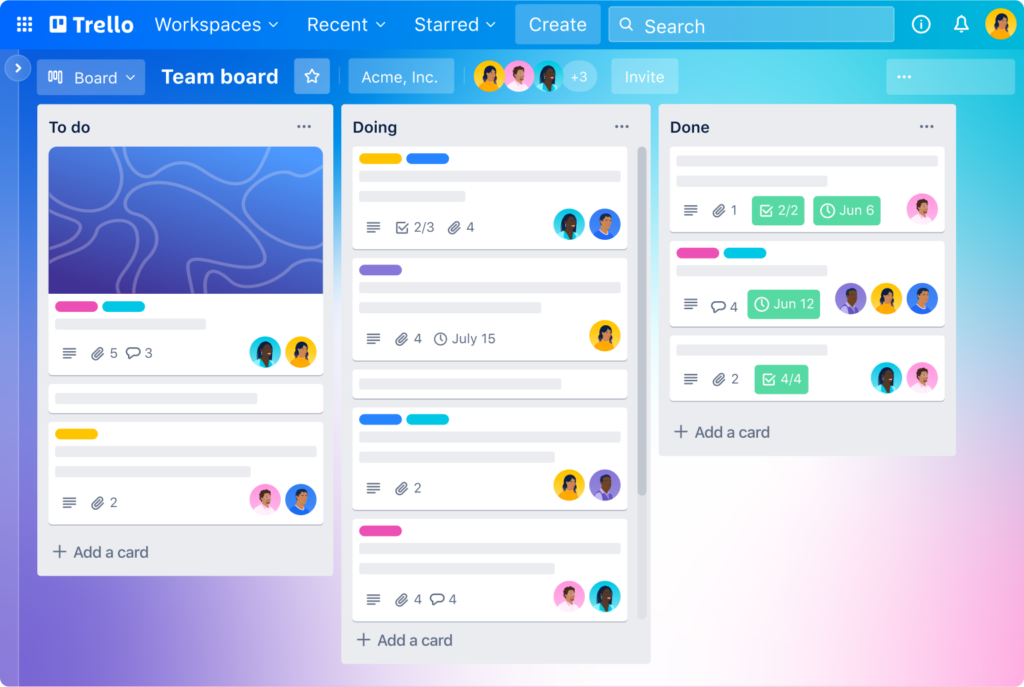
Trello
Trello is a flexible tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize tasks and milestones.
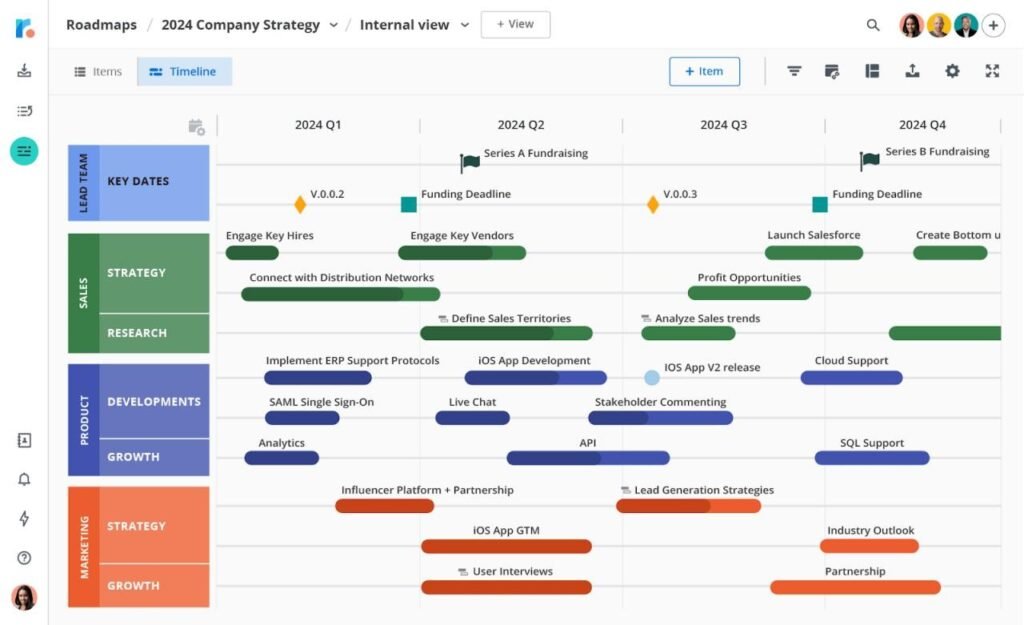
Roadmunk
Roadmunk is a tool that allows you to create beautiful, visual roadmaps with a focus on collaboration.
Aha!
Aha! is a great product when it comes to roadmaps focused on strategic alignment. It is well-suited for large organizations with complex product portfolios.
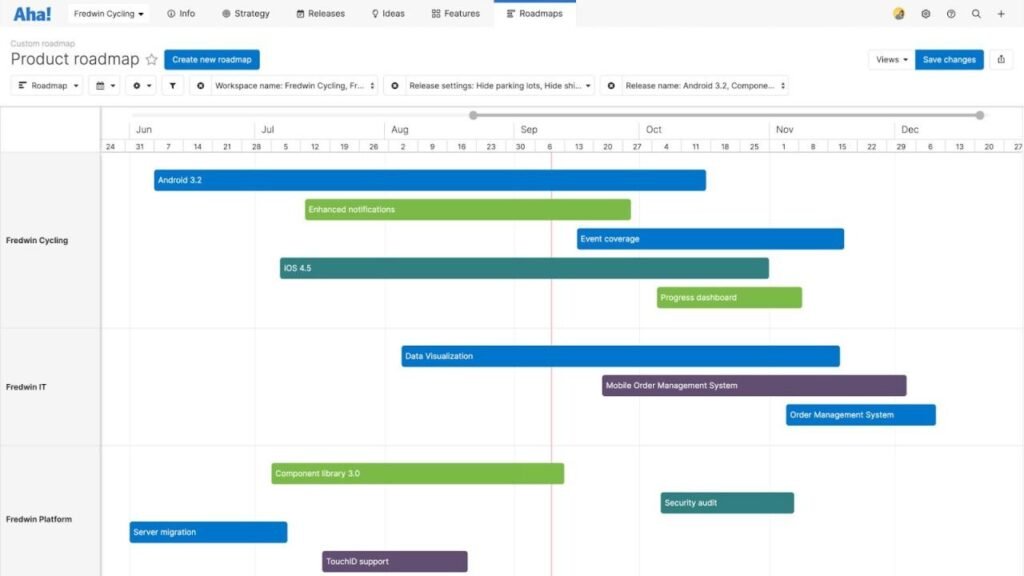
Best Practices and Frameworks
Engage with Stakeholders

Product roadmaps are a collaborative effort. You need to engage with key stakeholders in your organization, from leadership to development teams to sales and customer support. These stakeholders provide valuable insights and perspectives to help ensure that your roadmap is comprehensive and aligned with business objectives.
Prioritize Wisely
Prioritization can often be tricky and easy to mess it up given its complexities. This is why it is essential to work through the process of prioritization thoroughly. You need to evaluate your product’s features and initiatives based on their impact, feasibility, and alignment with your product’s vision and goals. Using frameworks such as RICE and MoSCoW methods can be valuable but remember to choose the prioritization framework that works for your team and doesn’t introduce unnecessary complications. Simply start with Value vs. Effort framework and if it’s good enough, stick with it.
Select the Right Format
Choosing the right roadmap format is key for effective communication to your team. It ensures that the goals and plans are clearly understood and helps align with the expectations of different stakeholders. Here are two examples of roadmap formats:
- Feature-Based Roadmap
A Feature-Based Roadmap focuses on specific features, enhancements, and fixes planned for a product over a certain period. It focuses on the what and when of product development. This roadmap is typically used for keeping the product development on track by understanding the sequence of feature releases, which allows the team to prepare accordingly. Templates from Aha!
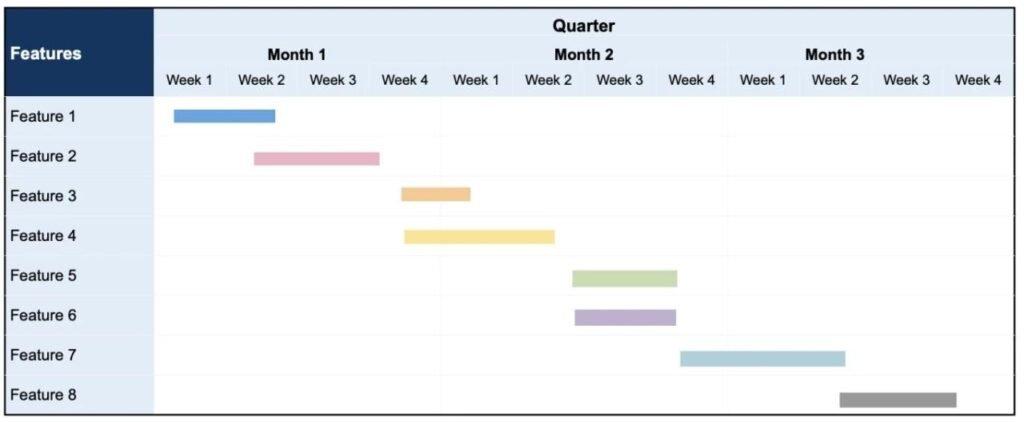
- Strategy Based Roadmap
This roadmap focuses on high-level strategic goals which guide the product’s direction. The Strategy Based Roadmap is most helpful in outline the why behind a product and it’s development. It is typically used to communicate the strategic direction of the product to high-level stakeholders without having to go down to the specifics. Templates from Roadmunk.
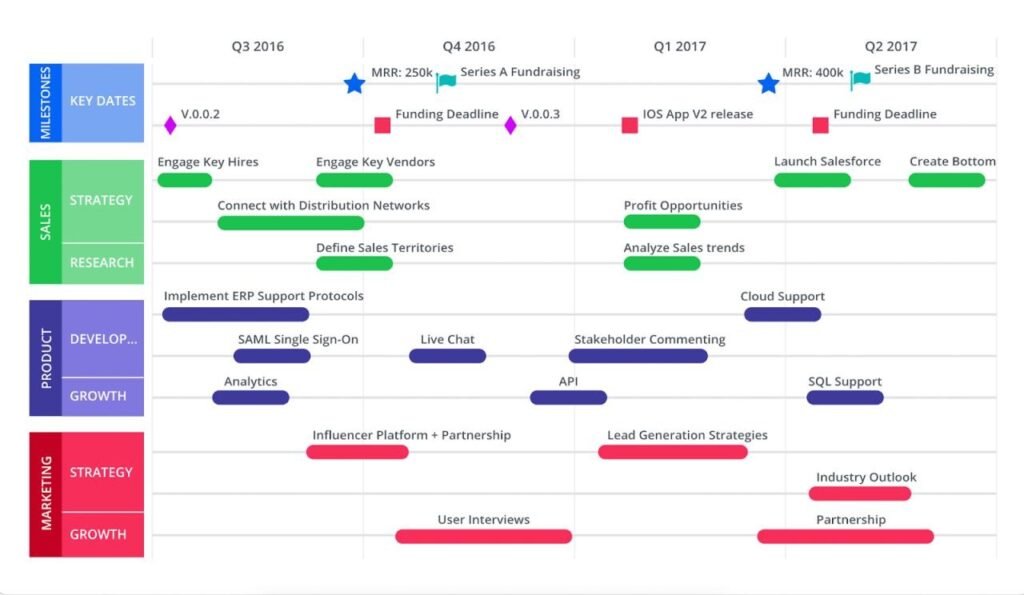
Review and Iterate
Building your roadmap is an iterative process, which is why it is crucial to review it with key stakeholders, such as management, development and design teams. Their feedback is needed to make the necessary adjustments in order for the roadmap to be effective and accurate.
Communicate and Implement
Once the roadmap is finalized, it needs to be communicated across teams in your organization. You need to ensure that everyone knows and understands their role in implementing the roadmap and how it aligns with the overall product strategy. The roadmap needs regular updates and reviews to be able to adapt to any necessary changes.
Always Learn and Adapt
Roadmaps are living documents and should adapt based on customer feedback, changes in the market, and new information. It is essential to establish regular review cycles for the roadmap and adjust priorities and timelines as needed.
>> Subscribe to PRODUCT360 Newsletter to get Product Management’s insights, latest trends, frameworks, and best practices in the industry.





